What is the relationship between Artificial Intelligence – AI, Machine Learning – ML, Deep Learning, Natural Language processing – NLP, Generative AI – Gen AI?
- AI is the overarching field, which encompasses everything that falls under human-like intelligence, including both ML and NLP.
- ML is a subset of AI, and within ML, Deep Learning is a specialized approach to solving problems using neural networks.
- Deep Learning is particularly useful in tasks like image recognition, speech processing, and natural language understanding, making it a significant tool within NLP.
- Generative AI sits at the intersection of AI and deep learning, focusing on models that create new content, and can be used in NLP for tasks like text generation.
- NLP is a specialized area within AI focused on language, and it often utilizes ML and Deep Learning techniques to achieve language understanding and generation.
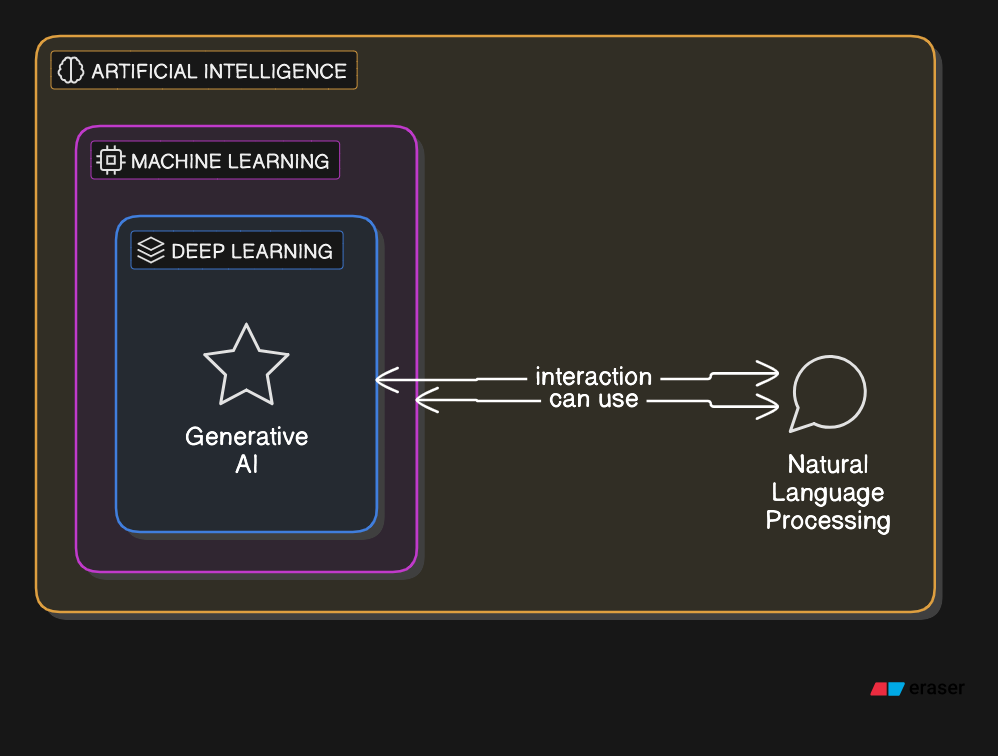
Summary:
AI is the broad field that includes everything related to simulating human intelligence.
ML is a subset of AI, focused on learning from data.
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of ML that uses deep neural networks.
NLP is an AI field focusing on language and often relies on machine learning and deep learning techniques.
Generative AI creates new content and can be powered by deep learning models.
What is the difference between Regression and Inference?
Regression
Definition:
Regression is a statistical technique used to model and predict the relationship between a dependent variable (target) and one or more independent variables (predictors). It is primarily used to make predictions based on data.
Example:
Imagine you are a real estate agent trying to predict the price of a house based on its size (in square feet). If you collect data on several houses, with their size and price, you could use regression to find the equation that predicts the house price based on its size.
- Equation:
Price = 50,000 + 200 * (Size in square feet)
This equation tells you that for every additional square foot, the price of the house increases by 200 units.
Inference
Definition:
Inference is the process of drawing conclusions about a population based on sample data. It involves statistical tests to make generalizations or estimate the parameters of a population. The goal is to test hypotheses and understand relationships between variables.
Example:
Suppose you want to know whether a new teaching method improves student test scores. You take a sample of students, apply the new teaching method to them, and then compare their scores to a control group that used the traditional method. You would use inference to test whether the difference in test scores is statistically significant.
- Hypothesis Testing:
- Null Hypothesis: The new teaching method has no effect.
- Alternative Hypothesis: The new teaching method improves test scores.
Key Differences Between Regression and Inference
| Aspect | Regression | Inference |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Predicts the value of a dependent variable | Draws conclusions about a population from a sample |
| Focus | Focuses on prediction and modeling relationships | Focuses on understanding and testing hypotheses |
| Outcome | Produces a predictive model (e.g., an equation) | Produces conclusions (e.g., p-values, confidence intervals) |
| Example Question | What is the expected price of a house based on its size? | Does the new teaching method improve student test scores? |
| Type of Data | Typically uses continuous data for prediction (e.g., salary, temperature) | Often uses sample data to make conclusions about a population |
| Method | Involves fitting a model to data (e.g., regression line) | Involves statistical testing (e.g., t-tests, ANOVA) |
| Goal | To predict future or unknown outcomes | To test a hypothesis or estimate population parameters |
| Output | A model with coefficients (e.g., slope, intercept) | P-values, confidence intervals, and estimates |